Decaf coffee is a popular alternative to regular coffee, catering to those who want to enjoy its taste without the potentially negative effects of caffeine.
Decaffeinated coffee undergoes a process to remove most of the caffeine content, providing a lower-energy beverage while maintaining the flavor associated with coffee.
As a result, many people are curious about the calorie content of decaf coffee and how it compares to that of regular, caffeinated coffee, espresso.

Although decaf coffee contains some calories, it’s typically a negligible amount, much like its regular counterpart.
According to Nutritionix, an 8-ounce serving of decaf coffee has only 3.6 calories and 0.8 grams of carbohydrates.
Meanwhile, FatSecret reports that a similar serving size contains just 2 calories.
The slight differences in reported calorie content may arise from variations in decaffeination processes and coffee bean types, but overall, decaf coffee remains a low-calorie beverage option.
Key Takeaways
- Decaf coffee is low in calories, with only 2-3.6 calories per 8-ounce serving.
- The decaffeination process helps retain coffee flavor while reducing caffeine content.
- Additions like milk, sugar, and syrups can increase the calorie count of decaf coffee substantially.
Decaf Coffee Calories
Decaf coffee drink is a popular choice for those looking to enjoy a cup of coffees without the stimulating effects of caffeine. But, is it really any different than regular coffee when it comes to calories?
Let’s explore the calorie content of decaf coffee and how it compares to regular coffee.
A cup of black decaf coffee has very few calories – only around 2 calories per 8-ounce (240ml) serving. This is nearly identical to the calorie content of regular black coffee.

The negligible calorie count is due to the fact that coffee, whether caffeinated or decaffeinated, is predominantly made up of water, containing only trace amounts of fats and carbohydrates.
It is important to note that the calories in decaf coffee can increase significantly depending on the additives one chooses to include.
For example, adding sugar, milk, or cream to your decaf coffee will increase the calorie content.
A tablespoon of sugar adds around 48 calories, whole milk adds 9 calories, and heavy cream adds a whopping 52 calories per tablespoon.
Now, let’s consider flavored decaf coffee. Generally, it is assumed that the calories in flavored decaf coffee remain low if the flavors are derived from the coffee beans themselves.

A brewed flavored coffee may contain around 2 calories per 8 ounces (240 mL) – similar to that of plain decaf coffee. However, this may vary depending on the brand and type of flavored bean used.
In summary, decaf coffee on its own contains minimal calories. However, the additives and flavorings can significantly affect the calorie content.
To keep their decaf coffee low in calories, one should be mindful of the ingredients they add to their cup.
Understanding Decaffeination
Decaffeination Process
Decaffeination is a process that removes most of the caffeine from coffee beans to produce decaffeinated coffee.
This is usually done using solvents like methylene chloride or organic solvents that selectively extract caffeine from the beans.
The decaffeination process generally removes about 97% of the caffeine content, leaving decaf coffee with around 2 mg of caffeine per cup.

Coffee beans are initially green and packed with chlorogenic acid, a natural antioxidant. During the decaffeination process, the green coffee beans are soaked in the solvent, which draws out the caffeine.
Once the caffeine is extracted, the solvent is removed, leaving the beans with minimal levels of caffeine. The beans are then roasted, which results in the familiar aroma and taste of coffee.
Alternative Methods
Apart from the use of solvents, there are alternative methods for decaffeinating coffee beans. One such method is the Swiss Water Process, which relies on water and carbon dioxide to extract caffeine.
The green coffee beans are soaked in water, which removes not only caffeine but also flavor compounds and oils.
The water is then passed through a carbon filter that captures caffeine molecules while allowing flavor and oils to return to the beans, ensuring a tasty and aromatic decaffeinated coffee.
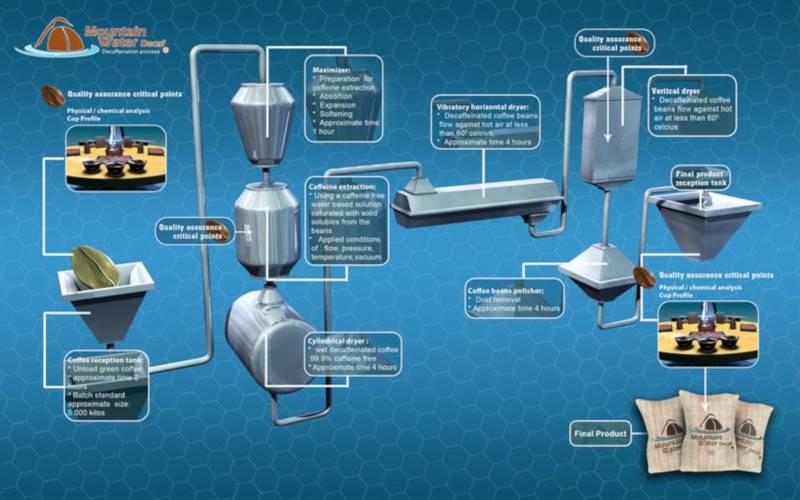
Another approach is the carbon dioxide method, where carbon dioxide is used to draw out caffeine from the beans.
In this process, coffee beans are subjected to high pressure and carbon dioxide, which binds to caffeine molecules, effectively removing them from the beans.
The residual carbon dioxide evaporates, leaving behind decaffeinated coffee with its inherent flavors and aromas.
While decaffeination removes most of the caffeine content, it’s important to note that decaf coffee is not entirely caffeine-free.
Decaf coffee still provides nutritional benefits such as antioxidants, making it a suitable choice for those who wish to enjoy coffee without the stimulating effects of caffeine.
Nutritional Comparison
Nutrition and Ingredients
Decaf coffee and regular coffee share many similarities in terms of nutritional content. Both types of coffee contain minimal amounts of calories, fat, and sugar.
A typical serving of decaf coffee has only 2 calories, while regular coffee has slightly more.
The main difference between the two lies in their caffeine content, with decaf coffee having significantly less caffeine compared to its regular counterpart.
Both decaf and regular coffee contain trace amounts of essential nutrients such as potassium, magnesium, and niacin.
However, these amounts are quite insignificant and do not contribute much to the daily recommended intake, general nutrition advice.
Additionally, both types of coffee have minimal amounts of protein, fat, sugar, sodium, carbohydrates, and cholesterol, making them a negligible source of these dietary components.
Serving Sizes
When comparing the nutritional content of decaf and regular coffee, it is crucial to consider serving sizes.
The standard serving cup for coffee is usually 8 fluid ounces or 1 cup.
In this serving size, decaf coffee has about 2 calories and 0.24g total carbohydrates, while regular coffee contains slightly more calories and a similar amount of carbohydrates.
The nutritional profile of both types of coffee can be affected by the brewing method, the type of coffee bean used, and any additives like sugar, cream, or milk.
It’s essential to understand the nutritional information listed on food labels is based on standard serving cups and can vary depending on personal preferences and serving variations.
In summary, decaf and regular coffee are similar in terms of nutritional content, with the primary contrast being their caffeine content.
Both beverages contain minimal calories, fat, sugar, and sodium, making them an enjoyable daily treat for most people without significantly impacting their daily nutrient intake.
| Coffee Type | Calories (per 8 oz) |
|---|---|
| Decaf Brewed Coffee | 2 |
| Decaf Instant Coffee | 2 |
| Decaf Espresso | 2 |
| Decaf Cappuccino | 70 |
| Decaf Latte | 135 |
| Decaf Mocha | 180 |
Caffeine Content Difference
Decaf Vs. Regular Coffee
Decaffeinated coffee, or decaf, undergoes a process to remove most of the caffeine content from the beans.
This results in a beverage that contains only a small amount of caffeine, making it a popular option for those who want to limit their caffeine intake.
Decaf coffee typically contains about 2 mg of caffeine per serving, compared to the approximate 95 mg of caffeine found in a regular cup of coffee.
There are several methods used to decaffeinate coffee beans, with each having a similar outcome.
The goal is to create a product that contains at least 97% less caffeine than its regular counterpart, while still preserving the beans’ natural flavor and aroma.
When comparing caffeine levels in various types of coffee, it’s important to consider the serving size.
Decaf coffee may have small amounts of caffeine, but when consumed in moderation, it can significantly reduce your overall caffeine intake.
It is also worth noting that caffeine content can vary depending on factors like brewing time and preparation methods.
Using these numbers as a guideline can help you make more informed choices about your coffee consumption.
In summary, the primary dissimilarity between decaf and regular coffee is the amount of caffeine.
Decaf coffee contains only a fraction of the caffeine present in regular coffee, making it a suitable option for those who wish to limit their caffeine consumption.
However, it is essential to remember that decaf coffee is not entirely caffeine-free, and paying attention to serving sizes and preparation techniques can ensure a better understanding of your total caffeine intake.
Health Aspects
Benefits
Decaf coffee offers several health benefits to those who are sensitive to caffeine or looking for an alternative to regular coffee.
One significant advantage is that decaf coffee may protect against liver disease, heart disease, and type 2 diabetes without the side effects of caffeine source.
It can also help reduce anxiety, restlessness, and insomnia that some people experience when consuming caffeinated beverages.

Decaffeinated coffee is generally less acidic than regular coffee due to the decaffeination process removing some acidic compounds source.
This makes it a safer option for individuals with sensitive stomachs or those who suffer from heartburn, acid reflux, or other gastrointestinal issues.
Side Effects
While decaf coffee has its benefits, there are potential side effects to be aware of as well. Some chemicals used in the decaffeination process, such as methylene chloride, may pose health risks if consumed in large quantities.
Inhalation exposure to this chemical can irritate the nose, throat, and affect the nervous system source.
Additionally, decaf coffee may still contain small amounts of caffeine, which could cause problems for those who are extremely sensitive to caffeine or suffer from specific health conditions.
It’s essential for individuals with caffeine sensitivity, pregnant women, children, and those taking prescription medications to consult with a healthcare professional before consuming decaf coffee.
Other possible negative side effects include increased heart rate and blood pressure, although these tend to be less common in decaf coffee compared to regular coffee.
Nevertheless, those with pre-existing conditions or concerns about their heart health should discuss their coffee consumption with their healthcare provider.
In conclusion, decaf coffee can be a good option for those who are sensitive to caffeine, have stomach issues, or are seeking potential health benefits without the negative effects of caffeine.
However, individuals should consider their own health and discuss with a healthcare professional before making the switch to decaf.
Variations in Decaf Coffee
Beverages
Decaf coffee can be found in various forms and beverages, such as lattes, espressos, and brewed coffee. In a typical black decaf coffee, there are only about 2 calories per 8-ounce cup.
This low-calorie count is mainly because it consists of 99.9% water.
When other components like milk or cream are added to decaf coffee, the calorie count will increase. For instance, a decaf latte may have a higher caloric content due to the milk added.
Nevertheless, since decaf coffee has no sweet and low carb content, it can be a healthier alternative to traditional caffeinated coffee.
Furthermore, instant decaf coffee offers a convenient option for those who crave the taste and smell of coffee but want to avoid caffeine.
Just like brewed decaf coffee, instant decaf coffee’s caloric content mainly comes from trace amounts of carbs and protein.
Brands
Different brands of decaf coffee may have slight variations in flavor, color, and caloric content, but these differences are generally marginal.
For example, a serving of Starbucks’ decaf coffee may have 3 calories, while other brands may only have 2 calories per serving.
Decaf coffee regulations ensure that the caffeine content is adequately reduced, and various processing methods may impact the overall characteristics of the final product, including taste and aroma.

However, such changes do not significantly affect the calorie count.
In summary, decaf coffee presents a low-calorie alternative for individuals who want to enjoy the experience of drinking coffee without the caffeine.
Its caloric content is primarily influenced by added components like milk or cream, and potential variations across brands are minimal.
Adding Extras
When it comes to decaf coffee, the beverage itself is almost calorie-free. However, the calories can quickly add up when you start introducing extras like syrups, chocolate, and added sugars.
It’s essential to be conscious of these additions, especially if you’re trying to maintain a healthy diet or manage conditions like kidney disease.
Syrups are often used to enhance the flavor of decaf coffee drinks such as cappuccinos and lattes.
While they can provide a delightful burst of flavor, they also contribute significantly to the overall calorie count.
For instance, a single tablespoon of flavored syrup can contain anywhere between 50 to 100 calories, depending on the brand and flavor.
Chocolate, another popular add-on in decaf coffee drinks, can also contribute to the calorie count.
A tablespoon of powdered hot chocolate mix typically has around 70 calories, while chocolate syrup can increase 50 calories or more per tablespoon.
Added sugars are another concern when it comes to the calories in decaf coffee beverages. A single teaspoon of sugar contributes 16 calories, and many coffee drinkers tend to use more than one teaspoon.
Moreover, research has shown that almost 85 percent of calories from add-ins come from sugar, which can be particularly harmful for individuals with kidney disease or those watching their sugar intake.
It’s crucial for researchers and consumers alike to recognize how the calories in decaf coffee can significantly increase with the addition of extras like syrups, chocolate, and added sugars.
By being aware of these factors and making conscious choices regarding the ingredients in your coffee, you can enjoy a tasty beverage without sabotaging your health goals or worsening existing conditions.
FAQ
Is decaf coffee less calories?
Yes, decaf coffee generally has fewer calories than regular coffee.
This is because decaf coffee is made by removing caffeine from regular coffee beans, which means it has fewer compounds that contribute to calories.
Does decaf coffee have any calories?
Yes, decaf coffee still has some calories. While decaf coffee has fewer calories than regular coffee, it still has some calories due to the natural oils and compounds present in coffee beans.
Is decaf coffee OK for weight loss?
Decaf coffee can be a good choice for weight burn, loss because it has fewer calories than regular coffee.
However, it’s important to note that adding lot of cream, sugar, or other sweeteners can increase calories and negate the weight loss benefits of decaf coffee.
At the end of the day, it’s best to enjoy decaf coffee black or with a small amount of low-calorie sweetener.

