Coffee beans are roasted seeds of the coffee plant, and they are what give coffee its unique flavor. But are coffee beans legumes? What is a coffee bean considered?
Coffee beans are not legumes.
This might surprise you because coffee beans are often grouped with other beans, such as black beans, pinto beans, and lentils, which are legumes.
However, coffee beans are actually seeds, and they come from the fruit of the coffee plant.
To understand this topic better, this article will explore how coffee compares to:
- Fruits
- Berries
- Nuts
- Vegetables
But before we jump into all of that, let’s start with a brief overview of the coffee plant.
Overview of the Coffee Production Process
The reason why we need to understand the coffee production process is that it will help explain why coffee beans are not legumes. So, let’s take a quick look at the process from growth to cup.
Growing Coffee
The coffee plant is a flowering shrub that belongs to the Rubiaceae family.
There are over 100 species of coffee plants, but the two main types are Coffea arabica and coffee canephora.
Coffea arabica, also known as arabica beans, account for 60-80% of the coffee beans produced globally.
They are typically grown at high altitudes and have a milder flavor.
Coffea canephora, also called Robusta beans, make up the remaining 20-40% of global coffee production. These beans are hardier and have a more bitter flavor.
Coffee plants are typically grown in tropical regions like Central America, Africa, and Southeast Asia. The coffee plant grows best in places that have:
- High altitudes
- Ample sunshine
- Humid weather
- Well-drained soils
Coffee trees produce fruits called coffee cherries. It takes about 3-5 years for a coffee tree to mature and produce coffee cherries.
Coffee cherries take around 6-9 months to mature. Once they’re mature, they’re typically bright red or deep purple fruits. The coffee cherries usually contain two seeds, each of which is surrounded by a sweet pulp.
Harvesting Coffee
The coffee cherries are typically hand-picked or stripped off by machines to ensure that only the ripe cherries are harvested.
After they’re picked, the coffee cherries are transported to a processing facility.
Processing Coffee
There are two main types of coffee processing techniques: dry processing and wet processing.
Dry processing is the traditional method and it involves leaving the coffee cherries out in the sun to dry. This can take up to 4 weeks, and it results in a coffee bean that has a fruity flavor.
Wet processing is a more modern method, and it involves soaking the coffee cherries in water. This helps to remove the flesh of the cherry from the coffee bean.
The wet method is typically quicker than dry processing, and it results in a coffee bean that has a cleaner flavor.
Anaerobic processing has also become popular in recent years.
After the coffee cherries have been processed, the coffee beans need to be hulled. This is done by using a machine to remove the outer layer of the coffee bean.
The coffee beans are then sorted by size and weight. The beans that are the same size and weight are typically packaged together and sold as a specific coffee grade.
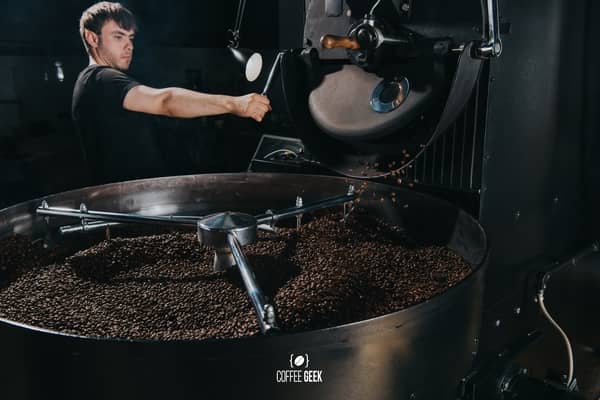
Roasting Coffee
After the coffee beans have been sorted and graded, they’re ready to be roasted. Roasting is a critical step in the coffee-making process because it brings out the flavor of the coffee bean.
Coffee beans are typically roasted at temperatures between 188 and 282 degrees Celsius (370 and 540 degrees Fahrenheit).
The roasting time varies depending on the desired flavor, but it is usually between 10 and 15 minutes.
After the coffee beans have been roasted, they are cooled and then packaged. The roasted coffee beans can be ground and brewed at this point, or they can be stored for later use.
As you can see, the coffee production process is quite involved. But what does this have to do with coffee beans and legumes?
Let’s first take a look at what a legume is.
What Are Legumes?
Legumes are a type of plant that belongs to the Fabaceae family. This family is also known as the pea family or bean family.
Some common examples of legumes include beans, peas, lentils, and peanuts. Legumes are characterized by their seed pods, which split open when they mature.
And that’s where coffee beans differ from legumes. Coffee beans are not contained in a pod, and they don’t split open when they mature. Instead, coffee beans are simply the seeds of the coffee fruit.
So, Are Coffee Beans Legumes or Beans?
The term “coffee bean” is actually a misnomer. The word “bean” is used because coffee seeds resemble true beans. However, they aren’t actually beans.
As explained in the production process above, coffee beans are the seeds of the coffee fruit. So, they aren’t technically beans, but the coffee seeds are often referred to as beans because of their similarities in appearance to true legumes.
How Does Coffee Compare to Other Plants?
Let’s now take a look at how coffee stacks up against some other popular plants by answering the question, “Is coffee a fruit, berry, nut, or vegetable?”
Are Coffee Beans a Fruit?
Coffee beans are not legumes, but are they a fruit? No, coffee beans are not a fruit.
We’ll explain why coffee beans are not a fruit by taking a closer look at the coffee plant.
As we mentioned before, the branches of a coffee tree produce dozens of small, green fruits called coffee cherries.
These coffee cherries mature and turn red, orange, or yellow when they are ripe. Once the coffee fruit is ripe, the coffee beans inside are also ripe and ready to be harvested.
So, when farmers harvest coffee, they are actually picking cherry fruit, and from the fruit, they extract the green coffee beans. This means that coffee beans are the seeds of the coffee fruit.
And since coffee beans are not the fleshy part of the fruit, they cannot be classified as a fruit. They’re a part of the fruit, but they’re not the main event.
Are Coffee Beans Berries?
No, coffee beans are not berries either.
The word “berry” is used to describe a fleshy fruit that has seeds on the inside.
Examples of berries include grapes, tomatoes, eggplants, cucumbers, and bananas.
Just so you know, raspberries, strawberries, and blackberries are not true berries. These fruits are actually aggregate fruits, which means that they’re made up of many small fruits.
Coffee beans are not berries because they’re not fleshy. They’re dry and hard, and they do not have the juicy, fleshy texture that berries have.
Are Coffee Beans Nuts?
Again, the answer is no. Coffee beans are not nuts.
Nuts are a type of fruit that has a hard shell and a soft, edible center. To open a nut, you need to use a tool, such as a hammer or a nutcracker.
Coffee beans do have a hard shell, but they cannot be classified as nuts because they do not have a soft, edible center.
Also, the coffee cherry where the beans come from is soft and fleshy, not hard like a nut.
Meaning you don’t need force to open it.
The common types of nuts include hazelnuts, chestnuts, pecans, and acorns.
Fun Fact: From a botanical standpoint, walnuts and almonds are not true nuts. They’re actually drupes, which are a type of fruit that’s fleshy outside with a hard shell that contains the seed on the inside.
Are Coffee Beans Vegetables?
So far, we’ve established that coffee beans are not legumes, fruits, berries, or nuts. So, are they vegetables?
A lot of people think that coffee seeds are vegetables because we call them “coffee beans”. Because, as we all know, beans are a type of vegetable.
However, since the term “beans” in coffee is a misnomer, coffee “beans” cannot be classified as vegetables.
What Is the Difference Between Beans and Legumes?
The primary difference between beans and legumes is that while beans are seeds from different plants, legumes are plants that produce fruit of the same type.
This means that all beans are legumes, but not all legumes are beans. For example, lentils and soybeans are legumes, but coffee beans and cocoa beans are not.
What Is the Benefit of Comparing Coffee to Other Plants?
Understanding the difference between coffee beans and other types of beans is important. This is because the classification of food often dictates how it’s grown, processed, and sold.
For example, legumes are typically high in protein, while fruits are typically high in sugar. Vegetables can be either high in protein or high in sugar, depending on the type of vegetable.
This means that if coffee beans were classified as a legume, they would be marketed as high-protein food. And if coffee beans were classified as a fruit, they would be marketed as a sweet, sugary treat.
But since coffee beans are not legumes, fruits, berries, nuts, or vegetables, they are marketed as a unique food product with its own set of health benefits.
This is why it’s important to understand the difference between coffee beans and other types of beans. Knowing the difference can help you make better-informed decisions about what you eat and drink.
FAQs
Where Do Coffee Beans Come From?
Coffee beans come from coffee fruit, which is also known as coffee cherries. The coffee fruit is a small, red berry that grows on coffee trees.

When the coffee fruit is ripe, farmers pick it up and extract the green coffee beans from inside. These beans are then roasted to create the familiar brown coffee beans that we know and love.
Are Coffee Beans a Legume?
No, coffee beans are not a legume. While they taste great in your cup of coffee, the coffee bean is actually just a seed.
What Are the Four Types of Coffee Beans?
There are four main types of coffee beans: Arabica, Robusta, Liberica, and Excelsa.
Arabica beans are the most popular type of coffee bean.
They make up about 60% of the world’s coffee production and are known for their sweeter, more nuanced flavor.
Liberica and Excelsa beans are relatively rare, making up less than 1% of the world’s coffee production. Liberica beans have a fruity, floral flavor, while Excelsa beans have a nutty, chocolatey flavor.
Can You Eat a Coffee Bean?
Yes, coffee beans are edible. Coffee beans contain antioxidants and caffeine, which can boost your mood and energy levels and lower your risk of some chronic diseases.
However, it’s advisable not to eat too many coffee beans at once because they can cause side effects like headaches and insomnia.
How Are Coffee Beans Roasted?
Coffee beans are roasted in coffee roasters, which is a machine that heats the beans until they turn brown.
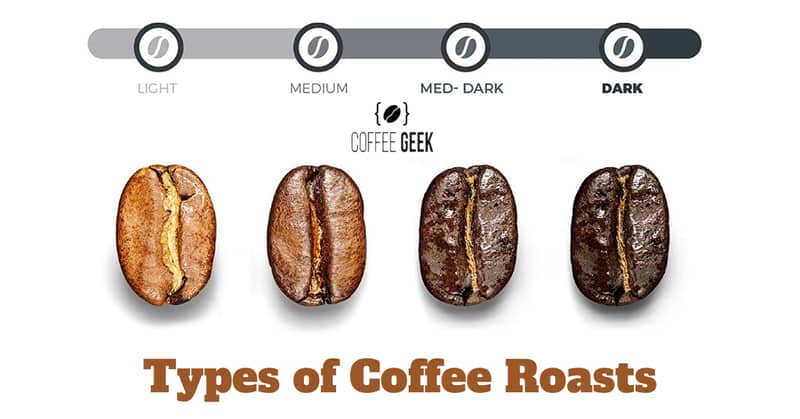
The type of roast (light, medium, or dark) determines how long the beans are roasted.
Lightly roasted coffee beans have a light brown color and a milder flavor, while darkly roasted beans have a dark brown color and a stronger flavor.
Medium-roasted coffee beans fall somewhere in between these two extremes.
If you want to get into the coffee roasting game, check out these home roasters to get started!
To Wrap Up
Coffee beans are not legumes. They are the seeds of the coffee fruit, which is also known as coffee cherries. So, the next time you’re enjoying a cup of coffee at your favorite coffee shop, remember that those beans are actually seeds!











